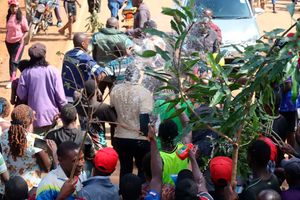Professionals offer expertise to identify potential issues and make informed decisions, ultimately saving homeowners time and money.
In Kenya, the aftermath of rains paints a grim picture: homes submerged, streets transformed into rivers and communities left to grapple with the devastation left by floods.
Wycliffe Waburiri, Chairperson of the Architects Chapter at the Architectural Association of Kenya, (AAK) shares invaluable insights with My Property on how to renovate homes to withstand extreme weather conditions.
What are the first steps homeowners should take when assessing damage to their homes after heavy rains?
Homeowners should prioritise safety by checking for gas leaks, electrical hazards, and structural issues, evacuating if necessary, and contacting emergency services. The next step is to document damage thoroughly with photos and videos and contact your insurance company promptly. Remember to perform inspections of the roof, gutters, walls, and interior for signs of damage or water seepage. Make temporary repairs to prevent further damage and remove standing water promptly.
You can also promote airflow and drying using fans and dehumidifiers, and remove wet materials to prevent mould growth. Inspect for mould and consider professional input if necessary. Depending on the damage extent, hire professionals like roofers or plumbers, and keep detailed records for insurance claims.
How important is it to have a professional assessment before starting any renovation?
Professionals offer expertise to identify potential issues and make informed decisions, ultimately saving homeowners time and money. Inspections target specific areas, such as structural assessments for foundations and roofing, electrical inspections for wiring and panels, and plumbing checks for pipes and fixtures, detecting potential leaks.
Which building materials do you recommend for enhancing the durability of homes against extreme weather?
The choice of building materials plays a crucial role in constructing a disaster-resistant home. While the aesthetics of your home are important, using durable materials that can withstand the forces of nature is more important. Materials such as reinforced concrete, natural stone, and steel offer better structural integrity and resistance against wind, water, and fire damage. For enhanced security against the elements, consider impact-resistant windows and doors, which can tolerate high winds and flying debris.
Are there specific construction techniques that can better protect a house from heavy rains and flooding?
Yes. These vary a great deal. For example, a foundation type is in itself a form of construction technology.
Depending on the type of soil, your engineer should be able to recommend a suitable foundation. It is recommended that buildings be constructed above the road level. The ground floor slab (plinth) must be raised above the ground level to prevent surface water from entering the building. Equally, stormwater from the compound should be channelled to the stormwater channels usually along the road to evacuate it to the natural reservoirs like rivers, dams, ponds, lakes and oceans.
How can architectural design be optimised to mitigate the impact of extreme weather conditions?
First site selection is crucial for construction projects, aiming to minimise exposure to hazards and utilise natural resources. Developers should avoid floodplains, steep slopes, and wildfire-prone areas while optimising solar gain and natural ventilation. Structures should be strong and durable, using reinforced concrete, steel, and fire-resistant materials. Envelopes should resist water, wind, fire, and seismic forces. Sloped roofs with overhangs, shutters, and vents prevent water infiltration and overheating. Design strategies like mixed-use and connectivity create vibrant neighbourhoods. Involving stakeholders in co-creating and managing projects humanises them, especially in times of tragedy.

Residents of 360 Phase 2 Estate in Syokimau wade across a flooded section of the estate after a heavy downpour on June 17, 2024.
What design techniques can help manage water flow and prevent damage?
Design elements and techniques are pivotal for managing water flow and preventing damage in buildings. Shedding involves sloping surfaces to efficiently drain water away from the structure, crucial for roofs, canopies, and window and door sills. Overhangs, particularly at critical areas like roof-to-wall transitions and entry points, divert water shedding away from the building envelope, shielding vulnerable sections and occupants from water ingress. Understanding surface tension and water runoff is essential. Throating and creating grooves in exterior surfaces, redirects water away from the building, discouraging infiltration.
Components like Z-flashing profiles above windows and doors direct water away, while drip edges at roof overhangs and window sills prevent water from clinging to surfaces. By integrating these features, architects and builders can effectively manage water runoff, safeguarding buildings from infiltration and damage. These design principles are crucial for maintaining structural integrity and mitigating the adverse effects of water intrusion, ensuring the longevity and resilience of the building against water-related challenges.
What are the cost implications of renovating a home to make it more durable against extreme weather?
These will depend on the extent of renovation work to be done. If your home was built in an area where the soil tends to swell with rains and contract during periods of drought, those changes put your foundation at risk. Foundation repairs are complicated and can get very expensive. The envelope of your house is crucial in keeping away the elements of weather. Load-bearing walls act as structural elements of the building. Where this is used, any form of cracks should not be ignored.
Your roof is the most important part of your house for protecting everything else in it from the elements. When it needs repair, it’s important to do it fast. Renovation should therefore be informed by professional expertise and in some instances, it may be less costly to bring down the house and build anew just like insurance companies write off cars in accidents.
Are there cost-effective solutions for homeowners who may not have a large budget for renovations?
Homeowners looking to manage water runoff and prevent water intrusion without a large renovation budget have several effective options. Installing weather stripping around doors and windows can prevent water from seeping inside during heavy rains and improve energy efficiency by reducing drafts. Improving the grading around your home by sloping the ground away from the foundation is another cost-effective measure.
This can be achieved through basic landscaping, using soil and a shovel to create a gentle slope. Adding drip edges, which are metal or plastic strips, can direct water away from the structure. Applying a high-quality waterproof sealant around windows, doors, and other openings significantly reduces the risk of water infiltration. Regular inspection and reapplication of the sealant will maintain its effectiveness.
Properly installed gutters and downspouts are essential for directing water away from the foundation of the house. It’s important to ensure gutters are clean and properly pitched, and adding downspout extensions can channel water further from the house. Creating gravel trenches around the perimeter of the house can help absorb and direct water away from the foundation.
This can be a cost-effective DIY project using gravel and landscape fabric. The cost of renovation is influenced by the cost of materials and equipment, as well as the building technology used. A balance between these factors will ultimately determine the renovation cost, therefore, routine maintenance may be the easiest and most effective solution for managing water runoff and preventing water intrusion.
How can sustainable practices be incorporated into renovations to make homes more resilient to weather conditions?
Incorporating sustainable practices into home renovations enhances resilience to weather conditions and benefits the environment. Use durable, weather-resistant, locally available materials. Apply passive design principles to maximise natural light and ventilation.
Improve water management with rainwater harvesting, permeable materials, and efficient drainage. Enhance landscape design with native plants for natural insulation and reduced irrigation needs. These strategies create eco-friendly, resilient homes.
What preventive measures can homeowners take to protect their homes from future extreme weather events?
Regularly check for weaknesses in your home’s roof, windows, doors, and garage doors, as strong winds and storms can exploit these weak spots. Reinforce your roof with strong support and metal materials to protect against extreme weather and maintain the structural integrity of your home. Invest in storm shutters or impact-resistant glass to fortify your windows against damage from strong winds and heavy rain. If you live in a flood-prone area, prioritise flood-proofing by making your home’s foundation, doors, and windows watertight and installing proper drainage systems to redirect water.
Finally, keep your yard clear of dry vegetation and unsecured heavy items that could become hazards during storms.
Are there any particular challenges unique to Kenya or specific regions within Kenya when it comes to weather-proofing homes?
Yes. Low-lying areas like Budalangi, Kisumu, Tana River, and Mombasa are prone to flooding, while North and North Eastern regions like Moyale, Turkana, and Garissa experience dry weather and occasional flash floods.
Weather-proofing in these areas is challenging due to local climate variability, making it complex to design effective solutions. Additionally, high-quality weather-proofing materials and techniques are costly, posing barriers for some due to initial expenses and technological challenges in installation and material selection.
How can local architecture and traditional building methods be adapted to improve durability against extreme weather?
This involves a blend of preserving cultural heritage and incorporating modern advancements. By leveraging local knowledge, enhancing structural integrity, optimising materials, and engaging communities, homeowners and builders can create resilient structures that withstand extreme weather while respecting traditional designs.
What is the role of building codes and regulations?
Building codes and regulations govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings, covering areas like fire safety, structural integrity, energy efficiency, and accessibility. They establish minimum standards and guide compliance. These regulations help make buildings resilient to natural disasters by minimising the risk of water damage, for instance, by requiring elevated foundations in flood-prone areas.
How can homeowners work with insurance companies to cover the costs of renovations for weather resistance?
Major renovations can significantly impact your existing insurance coverage and may even void it in some cases. For example, expanding your home’s square footage, adding features like a swimming pool, or upgrading electrical or plumbing systems can alter the value and risk profile of your property. If you don’t update your home insurance policy to reflect these changes, it may not provide adequate coverage in case of damage.
Before starting a home remodelling project, evaluate the changes you plan to make, such as adding square footage, installing a new roof, or upgrading the kitchen, as these can affect your home’s value. It is crucial to inform your insurer before beginning any renovations. After the renovation, reassess your home’s new replacement cost and adjust your coverage limits accordingly. Your insurer can assist with this process. It is also important to document the renovation by keeping receipts, contracts, and before-and-after pictures. We recommend contacting your insurance agent before, during, and after the home improvement project to ensure you have sufficient coverage.
Future trends in architecture for climate resilience?
Sustainable design in architecture aims to create buildings and communities with minimal environmental impact by using renewable energy, optimising natural light and ventilation, and incorporating eco-friendly materials. It also emphasises water conservation, waste reduction, and integrating green spaces for biodiversity and human well-being. Resilient architecture focuses on designing buildings that can withstand challenges like climate change and natural disasters. It involves using strong materials, advanced structural systems, backup power sources, and emergency preparedness measures to ensure buildings remain functional during crises.
How does AAK address extreme weather challenges in its guidelines?
The Architectural Association of Kenya has been advocating for safe and healthy homes. In 2022, in partnership with Habitat for Humanity, AAK published the “Healthy Homes: Guidelines and Checklist” which, while not specific to extreme weather, contributes to preventive measures for safe habitats during adverse conditions.
Additionally, AAK, in collaboration with the Royal Academy of Engineering, Kounkey Design Initiative, Arup East Africa, University College London, and Akiba Mahinani Trust, published the ‘Integrated & Inclusive Infrastructure Framework (3iF)’ for Kenya. This practical guidebook provides principles and tactics for infrastructure development, especially in informal settlements that often suffer from adverse weather.
In 2020, AAK formed the Flooding Resilience and Prevention in Kenya Taskforce to address the recurring loss of lives and livelihoods due to seasonal floods. This led to the launch of the ‘Crowdfunding for AAK Floods Resilience Project’, aimed at generating resources to publish a design guide, planning policies, and construction prototypes for flood-affected areas in Kenya.